Bad weather across Africa led to poor cocoa harvests, sparking hedge funds to bet big on a supply shortage by investing heavily in cocoa futures in London and New York. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) reports these speculators now hold a record-breaking USD 8.7 billion in cocoa market bets.
It’s upsetting considering we haven’t witnessed such a significant decrease in cocoa output in recent years,
told Samuel Adimado, the president of the Ghana cocoa buyers group to Anadolu Agency. And he also added:
Not only have we observed a drop in production, but we’ve also had to scale back our operations, including layoffs and the termination of contracts for some staff members.
These insights from a key industry figure underline the immediate impacts of the poor harvests on the cocoa market. While the hedge funds’ investments didn’t directly cause the rise in prices, they have significantly intensified the volatility in futures market prices. This situation showcases the powerful interplay between physical supply constraints and financial speculation in driving commodity prices.
The scenario points a broader trend in the cocoa market, where natural challenges and financial strategies merge, creating a volatile pricing environment. Speculative activities’ effect on prices shows how commodity markets respond dynamically to a mix of physical supply issues and financial maneuvers, illuminating the complex forces that drive global agricultural trade.
Cocoa’s Global Influence and Market Dynamics
Cocoa, originally from South America, notably the Upper Amazon, has significantly impacted civilizations from ancient times to today. Cocoa’s journey from a luxury drink to a key ingredient in confectionery began with technological evolutions like the melanger and conching machine.
Nowadays the cocoa market, worth $21.1 billion in 2022, is on a path to hit USD 26.3 billion by 2027, with top brands like Mars Wrigley, Ferrero Group, Mondelez, and Hershey. The sector is growing an exceptional 4.7% annual growth rate up to 2033, fueled by increasing demand in the food and beverage sector.

Similarly, the chocolate market, while closely linked to cocoa, reported earnings of around USD 128 billion in 2022, with expectations to climb to USD 161 billion by 2027. This forecasted expansion sheds light on the global chocolate obsession, highlighting cocoa’s important role. As the market continues to grow, the role of these leading companies becomes more significant, sparking discussions on sustainability, supply chain ethics, and the economic justice within cocoa-producing communities.
The Struggle and Environmental Concerns of Cocoa Production
Cocoa’s story roots South America and West Africa’s history, with the latter region is now the core in the global cocoa supply chain. Despite Africa’s leading role in cocoa production, the majority of its farmers grapple with poverty, barely making profits due to market and pricing issues.
Stuck with old farming methods and little to no investment in modernizing their practices, these farmers are vulnerable to environmental threats and diseases, worsened by climate change and phenomena like El Niño. The recent adverse weather in West Africa significantly damaged crops, leading to a predicted 400,000-ton shortfall for 2024 and highlighting the precarious nature of global cocoa supply.
Against these challenges, there’s a rising call for sustainable farming and fair trade in the cocoa industry. It aims to improve farmers’ lives and to secure cocoa supply for the future. However, achieving this shift demands collective action from all stakeholders – governments, corporations, and consumers – to tackle poverty, environmental harm, and market instability plaguing the sector.
Unprecedented Surge in Cocoa Prices
Cocoa prices soared incredibly, nearly doubling between January 1 and March 21, 2024. This leap highlights how unpredictable and volatile the market can be, especially for essential commodities like cocoa.
Record-breaking cocoa prices have emerged because the global supply dropped sharply, pushing chocolatiers to scramble for this crucial ingredient. GlobalData forecasts an 8% cut in the 2023-2024 season’s supply compared to the year before. The main reasons are heavy rainfall and diseases hitting the biggest suppliers, Cote d’Ivoire and Ghana.
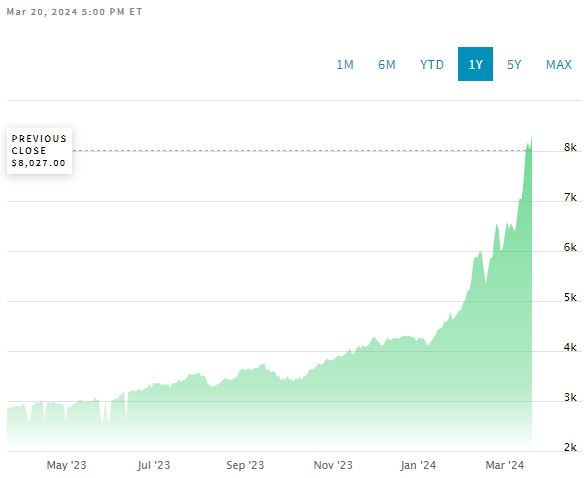
From the third week of March backward twelve months, we’ve seen cocoa bean prices jump by 166% and 189% in the New York and London futures markets, respectively,
Gerard Stapleton, a GlobalData agribusiness analyst, reported.
Since October 2022, the prices have rocketed by 221% and 223% after being relatively stable for the previous three-and-a-half years.
Facing these soaring costs, brands are finding ways to slash expenses and handle the rising prices. A Lindt & Sprüngli spokesperson explained to Just Food how these market conditions have hit hard:
Cocoa beans, sugar, and milk, our key raw materials, always fluctuate in price. But the rising costs, especially for cocoa, which nearly doubled in price last year to hit a record high on the London commodity futures exchange, pose a big challenge.
Yet, despite these hurdles, Lindt announced a 10.3% increase in sales, reaching Sfr5.20bn ($5.87bn) and a 17.9% jump in net income to Sfr671.4m, showing the company’s ability to thrive even in tough market conditions.
This sharp increase in prices not only underlines the significant influence of market forces on pricing but also prompts serious thoughts on the future of cocoa supplies and what it means for producers and consumers worldwide. As everyone involved navigates this unpredictability, the cocoa market continues to be a key area for close watch and analysis.
Navigating Cocoa’s Future: Market Logistics, Demand, and Outlook
Javier Blas, a Bloomberg opinion columnist and energy and commodities expert, believes this period of turmoil is not just a challenge but a necessary crisis.
The world needs higher prices to encourage the re-planting of millions of old trees — and take better care of the current ones,
he said in a recent post on X (formerly Twitter). His perspective sheds light on the importance of facing the current hardships to foster a more sustainable and productive cocoa industry in the future.
Cocoa’s journey from farm to consumer involves unique challenges, from manual harvesting and processing to navigating the complexities of international trade and marketing. With the demand for cocoa and chocolate products climbing, driven by health trends and emerging markets, the industry must balance this increasing demand with sustainable and ethical production commitments. This has led to a greater emphasis on product traceability and fair trade, with a consumer shift towards products reflecting these values.
Looking forward, the cocoa market is in trouble. Making things better will require fresh approaches to production, trade, and consumption, with dedication to fairness and sustainability. As the market moves forward, today’s decisions by industry players will form cocoa’s future, determining its ability to overcome current challenges and sustain its global significance.

