Monero often finds itself branded as the nefarious sibling among cryptocurrencies. Some jestingly call it the “go-to for criminals,” as it’s a privacy-focused cryptocurrency. But beyond these surface-level assessments, lies a digital currency with a unique technology that champions user privacy and anonymity.
What is Monero (XMR)?
Monero (XMR) is a decentralized cryptocurrency that prioritizes user privacy, fungibility, and decentralization and like Bitcoin and Ethereum it works on the Monero blockchain. Unlike many of its counterparts like Bitcoin, Monero transactions are confidential and untraceable. Every XMR unit is interchangeable and lacks a public record of its history, ensuring that its past cannot taint its present value.
Leveraging intricate cryptographic techniques, Monero provides a level of opacity that makes transaction details and participants unknown to outside observers, this is why XMR is so popular at the dark web, however it’s absolutely a legal cryptocurrency. While it borrows some principles from Bitcoin’s design and Bitcoin blockchain, it stands out due to its best unique privacy features, dynamic block size, and adaptive limits. The question then arises: What makes Monero tick? As we journey further, we’ll explore the technical nuances that give Monero its unique edge.

A Brief History of Monero
Monero’s journey, while relatively young, is rich in events and milestones that have shaped its present identity. Let’s explore its roots and the significant events that have marked its evolution.
- Origins: Monero’s story began in April 2014. It wasn’t an original creation but a fork of Bytecoin, the first currency written on the CryptoNote protocol. However, Bytecoin was plagued with controversies, particularly around its pre-mining. A group of developers decided to fork the blockchain, renaming this new branch “BitMonero,” which was shortly after simplified to “Monero,” Esperanto for “coin.”
- CryptoNote Foundation: Monero’s underlying technology borrows from the CryptoNote protocol, emphasizing anonymity. This protocol’s significance in Monero’s development cannot be overstated, as it laid the groundwork for features like ring signatures.
- Technological Advancements: Monero has seen several significant updates throughout its existence. From January 2017, Monero works by transitioning to RingCT, greatly improving its privacy features.. Later, in response to concerns about ASIC mining centralization, Monero’s developers made tweaks to its proof-of-work algorithm, ensuring it remains resistant to ASIC domination.
- Regulatory Scrutiny and Adoption: Given its potent privacy features, Monero has been both praised by privacy advocates and scrutinized by regulators and law enforcement agencies. While some exchanges have delisted Monero due to these concerns, it remains a favorite for those valuing privacy in transactions. Moreover, its adoption has grown beyond online transactions, with various vendors, both online and physical, accepting XMR tokens.
Monero’s history is a testament to its resilience and the community’s unwavering commitment to privacy and decentralization. From its origins as a fork to its present status as a beacon of transactional privacy, Monero continues to evolve, adapt, and grow in its mission.
Dark Web – The Dark Side of the Monero
Before we go into the Monero explanation in more detail, we’ll first give you a brief introduction to the dark-web. So what you can access on the internet through traditional browsers is just the tip of the iceberg. Everything else lies below it, also known as the deep web, which is no longer monitored by the well-known search engines like Google or Bing. This part is the dark web, the deepest layer, where encryption and anonymity are key, because this is where the underworld trade takes place, involving such horrors as drugs and arms trafficking.
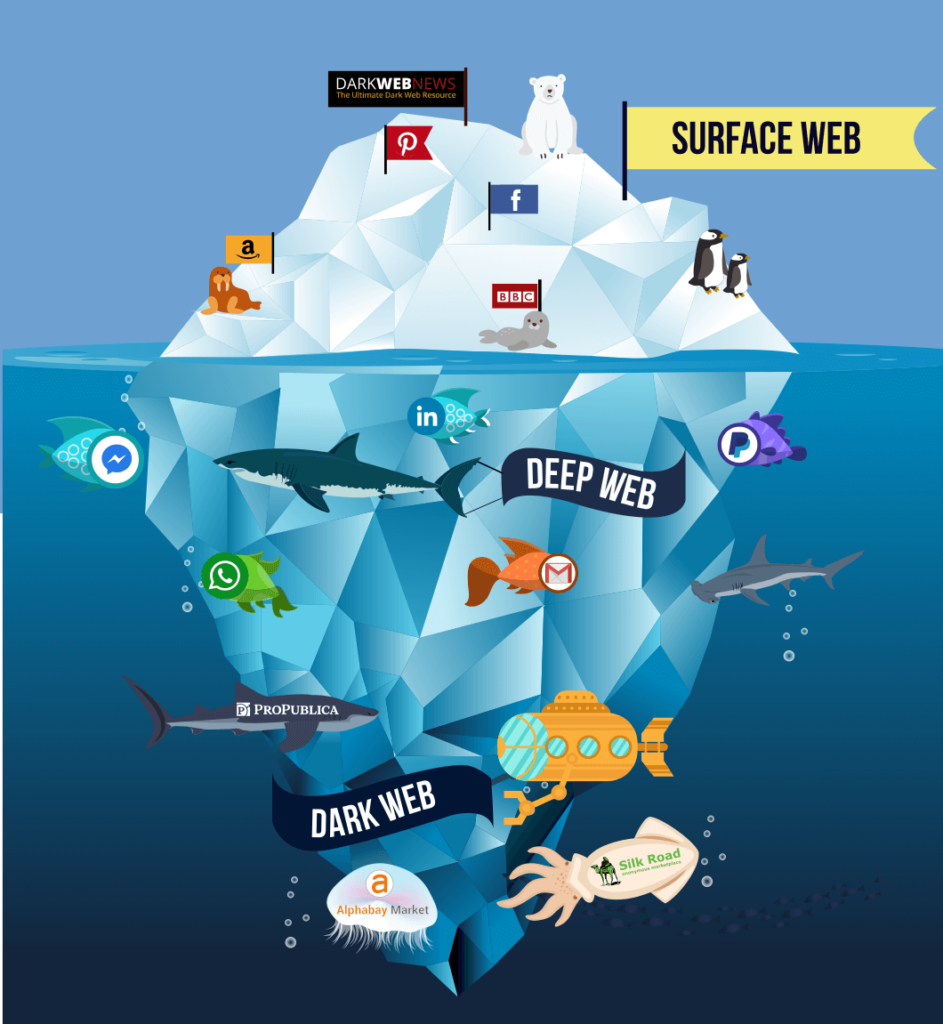
Now you can understand why altcoins like Monero play such an important role in this system. Access to the dark corners of the web is possible with special software like Tor, or I2P, which encrypts users’ data and reroutes their internet connection through several servers worldwide, obfuscating their digital footprints.
Whats the Difference Between the Cryptocurrency Monero and Bitcoin?
Bitcoin, often hailed as the original cryptocurrency, set the foundation for decentralized digital currencies. Yet, as the world of cryptocurrencies evolved, the need for more tailored solutions arose. Monero, while inspired by Bitcoin, diverged in several key areas to cater to specific demands around privacy and decentralization.
How Monero Different from Bitcoin?
- Privacy Mechanisms: Bitcoin transactions are transparent, meaning the amount transacted and the addresses involved are visible on its public ledger. Monero, as highlighted earlier, employs ring signatures, RingCT, and stealth addresses to ensure transactional privacy, making it inherently more private than Bitcoin.
- Mining Algorithm: Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 algorithm for its mining, which has led to the rise of specialized ASICs dominating the mining landscape. Monero, with its RandomX algorithm, resists ASIC dominance, promoting more egalitarian mining where individual users have a more leveled playing field against large mining farms.
- Supply Cap: Bitcoin has a fixed supply cap of 21 million coins, introducing a deflationary model. Once all bitcoins are mined, no new coins will be produced. Monero, on the other hand, follows a slightly different economic model. After the initial 18.4 million XMR is mined, a “tail emission” will kick in, producing a fixed 0.6 XMR per 2-minute block. This ensures miners are always incentivized to secure the network, even after the primary supply is exhausted.
- Adaptive Block Size: While Bitcoin has a fixed block size, which has occasionally led to scalability debates, Monero features an adaptive block size. This means that the Monero network can adjust its block size based on transaction volume, offering more flexibility and potentially smoother transaction processing during high-demand periods.
- Transparent Development: Bitcoin’s development, largely guided by a handful of influential figures, sometimes faces criticism for its opacity. Monero, on the other hand, champions a more transparent approach. Decisions around Monero’s development are made based on community consensus, and its funding is openly viewable, reinforcing the spirit of decentralization.
These distinctions, among others, carve out a unique space for Monero in the cryptocurrency world. While both Bitcoin and Monero share the overarching goal of decentralization, their paths diverge significantly when it comes to privacy, mining, and economic models.
Monero (XMR) Technicality Explained – Privacy Features and Anonymity
Monero’s distinctiveness in the realm of cryptocurrencies can be largely attributed to its sophisticated privacy-enhancing technologies. While we’ve touched upon them briefly, let’s dive deeper into the intricacies of Ring Signatures, RingCT, and Stealth Addresses to truly grasp how they safeguard user privacy.
- Ring Signatures:
- Concept: Originating from the world of public key cryptography, ring signatures are a type of digital signature where a member of a group possessing keys can sign on behalf of the group. In the context of Monero, it ensures the sender’s anonymity by mixing the sender’s input with several other inputs (past transaction outputs) present in the blockchain.
- Operation: When a user initiates a transaction, their digital signature is combined with those of others in the network. This creates a ‘ring’ of possible signers, obscuring the true origin of the transaction. As a result, outside observers cannot determine the real sender, as any member of the ring could have credibly signed the transaction.
- Ring Confidential Transactions (RingCT):
- Concept: RingCT builds upon the foundation of ring signatures but takes it a step further by concealing the transaction amount.
- Operation: Instead of openly broadcasting the transaction amount, RingCT transforms it into a cryptographic proof. This proof guarantees that the input amount is equal to the output amount without revealing the actual values. Only the sender and receiver can ascertain the exact transaction value, while to external observers, the amounts appear obfuscated.
- Stealth Addresses:
- Concept: A Monero adress, or stealth address is a one-time use address, ensuring that every incoming transaction to a Monero wallet uses a unique address not linked to the actual wallet address of the recipient.
- Operation: When a sender initiates a transaction, the Monero protocol generates a one-off address based on the recipient’s public key. The funds are sent to this temporary address. The recipient, with their private key, can detect and spend funds from this stealth address without revealing their actual wallet address. This ensures that even if third parties scrutinize the blockchain, they cannot link multiple payments to the same recipient.
These technological marvels form the bedrock of Monero’s privacy-centric approach. By intertwining multiple layers of cryptographic techniques, Monero assures that users can transact with peace of mind, knowing that their financial activities remain confidential and shielded from prying eyes.
Creating Money – Mine XMR and Investment Potential
Monero’s position in the cryptocurrency landscape isn’t merely rooted in its privacy and technological prowess. Its economic model, driven by mining and its perceived investment potential, has garnered significant attention. You can mine Monero using mining pools or in solo. Here’s a deep dive into the realm of Monero mining process and its investment prospects.
How to Mine Monero?
-
- Accessible Mining: One of Monero’s distinguishing features is its commitment to egalitarian mining. The RandomX proof-of-work algorithm it employs is specifically designed to be ASIC-resistant. This means that, unlike some other cryptocurrencies, mining Monero doesn’t require expensive specialized hardware. Regular CPU or GPU can effectively mine XMR, leveling the playing field and enabling more people to participate.
- Dynamic Block Size: With an adaptive block size, Monero adjusts its transaction processing capacity based on demand. This not only aids in scaling but also ensures that miners receive fair compensation for their efforts during high transaction volumes.

Investment Potential
-
- Unique Value Proposition: As privacy concerns mount in the digital age, Monero’s unwavering commitment to transactional anonymity offers a distinct value proposition. Unlike other cryptocurrencies where privacy is an option, Monero mandates it. This inherent trait could be an allure for investors who anticipate growing demand for private transactions.
- Limited Correlation with Bitcoin: While many altcoins often move in tandem with Bitcoin, Monero, due to its unique attributes and value proposition, sometimes showcases a limited correlation. This can make it an attractive diversification option for crypto investors.
- Regulatory Considerations: It’s crucial to consider the regulatory landscape when evaluating Monero’s investment potential. Given its enhanced privacy features, it has faced stricter scrutiny in certain jurisdictions, with some exchanges choosing to delist it. However, for some, this very trait underlines its value, especially in scenarios where financial privacy becomes paramount.
- Adoption and Integration: The broader the acceptance, the brighter the investment outlook. Monero’s adoption by various vendors and its integration into payment gateways and platforms contribute positively to its long-term potential.
In summary, Monero represents more than just a private coin. Its mining model upholds the spirit of decentralization, ensuring that individuals, not just mining farms, can benefit. As for its investment prospects, while the journey can be tumultuous due to external factors like regulatory stances, its intrinsic value as a privacy coin in an increasingly transparent world cannot be overlooked. Potential investors should always conduct thorough research and consider Monero’s unique position in the cryptocurrency arena.
Where to Buy Monero?
Cryptocurrencies like Monero are possibly declined by cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase, however most of them let it trade like Binance, Kraken or KuCoin. At the date of writing Monero’s price is $135.68. You only have to choose an exchange where Monero accepted and register an account. After a deposit (for example by using your Visa/Mastercard) you are able to buy this crypto coin. To stor the coin we highly recommend to use a cold wallet. Here you can find our detailed guide for crypto wallets!




